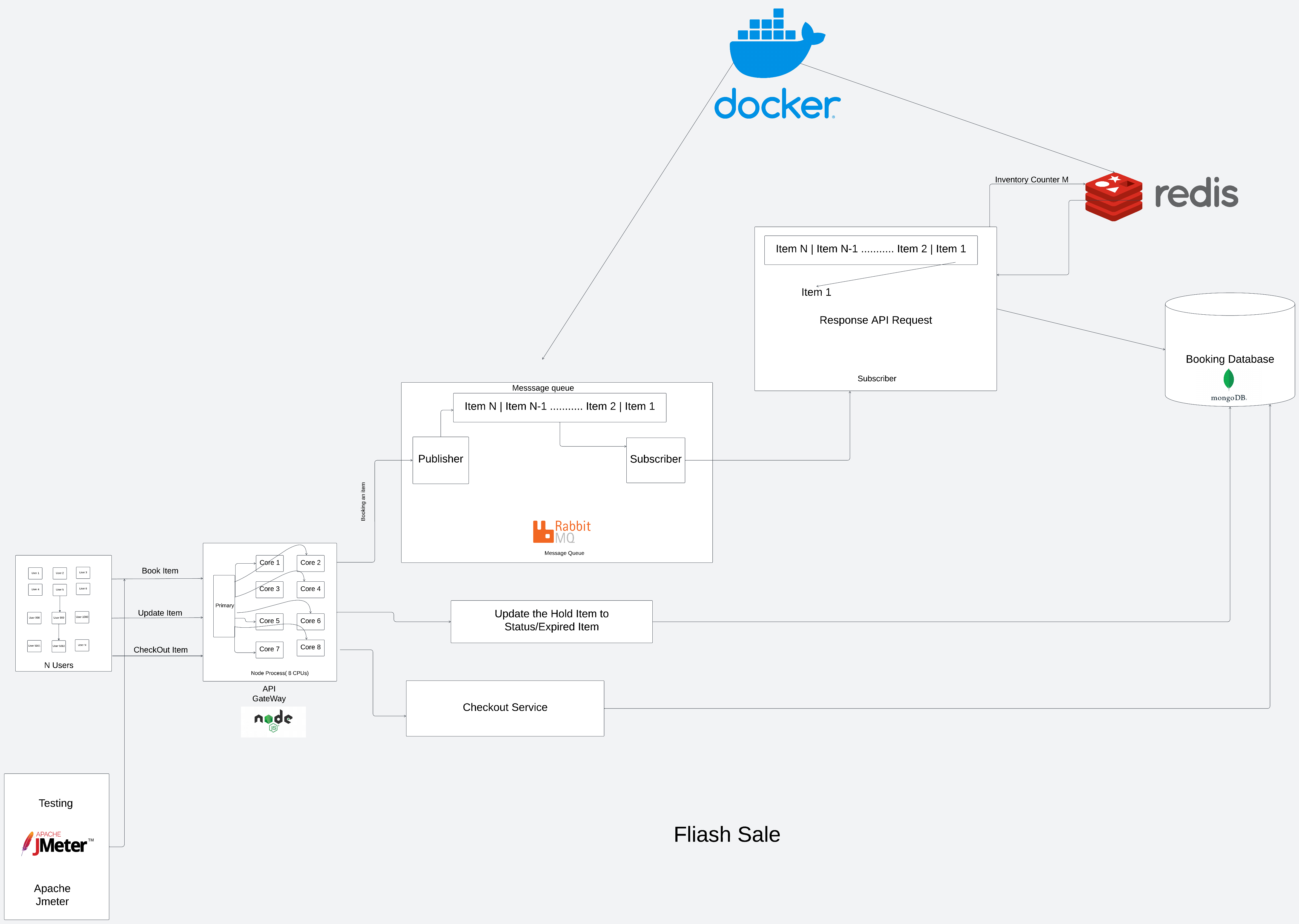
This document provides a detailed overview of the Flash Sale System implemented to handle high-concurrency scenarios, where a limited number of items are available for purchase, and a large number of users are attempting to buy them simultaneously.
- Inventory Size: The inventory size is limited, e.g., 1000 items.
- Traffic Load: The system should handle up to 1 million concurrent users attempting to purchase items.
- Inventory Consistency: The system must ensure that inventory is neither oversold nor undersold.
- Client Behavior: Users may refresh the page frequently or attempt to book items using scripts.
- User Authentication: All users are authenticated, and each user is allowed to purchase only one item.
- Request Queue: Incoming requests are managed via a message queue (RabbitMQ).
The system consists of several key components:
- Message Queue (RabbitMQ): To handle and buffer incoming requests, ensuring that the backend processes them at a controlled pace.
- Redis: Used for managing inventory counters and holding reservations.
- Backend Service: Node.js-based service responsible for processing requests, updating inventory, and managing bookings.
- Database: A persistent store (e.g., MongoDB) for storing booking records and tracking user transactions.
-
Request Handling:
- User requests are pushed to a RabbitMQ queue.
- The backend service consumes requests from the queue in a FIFO order.
-
Inventory Management:
- Redis is used for atomic inventory operations (
decr,incr). - Inventory counts are decremented as requests are processed.
- Redis is used for atomic inventory operations (
-
Booking Process:
- If inventory is available, the system creates a booking with a
holdstatus in the database. - The booking remains in the
holdstate for a fixed period (e.g., 5 minutes) until the user confirms the purchase. - If the user fails to confirm within the timeframe, the booking is canceled, and the inventory is incremented back.
- If inventory is available, the system creates a booking with a
-
Concurrency Handling:
- The use of Redis ensures atomic operations on inventory counters.
- RabbitMQ manages request processing speed to avoid overwhelming the backend.
-
Cheating Prevention:
- Each user is limited to one booking per sale.
- The system can track IP addresses and user agents to detect and prevent bot activity.
-
RabbitMQ:
- Manages the incoming booking requests.
- Provides a buffer to handle spikes in user traffic.
-
Redis:
- Manages the inventory count.
- Stores temporary holds on bookings.
-
MongoDB:
- Persists booking records with user and transaction details.
-
Node.js Backend:
- Handles business logic for the flash sale.
- Communicates with RabbitMQ, Redis, and MongoDB.
- RabbitMQ is used to manage booking requests. The queue
booking_requestsis created and configured for durability.
- Redis keys are structured as
inventory:<sale_id>:countfor inventory management andhold:<booking_id>for tracking holds.
- Booking Creation: If inventory is available, a booking record is created in MongoDB with a status of
hold. - Status Update: A PUT API updates the booking status to
bookedwhen the user confirms the purchase. - Cancellation: A DELETE API cancels a booking if the user fails to complete the purchase in time.
- Inventory Undersell/Oversell: Atomic operations in Redis prevent inventory mismatches.
- Queue Overflow: RabbitMQ manages the load to ensure that requests are processed at a manageable rate.
- Description: Updates the status of a booking from
on holdtobooked. - Request Body:
{ "status": "booked" }
- Description: Cancels a booking if it's not confirmed in time.
- Request Body:
{ "status": "deleted" }
- The system is designed to scale horizontally. Redis and RabbitMQ can be clustered to handle increased load.
- RabbitMQ provides durability and ensures that messages are not lost even if the service crashes.
- Caching strategies can be employed to reduce database load, e.g., caching item details.
This flash sale system is designed to handle high-concurrency scenarios efficiently, ensuring that inventory is managed accurately and that the system remains responsive under heavy load.
- Use of Redis Pub/Sub: To notify users in real-time when their booking status changes.
- Advanced Monitoring: Implement monitoring tools to track system performance and detect bottlenecks.
- Machine Learning: Predict user behavior and optimize inventory distribution.