Author/Maintainer: Amil Khan
After moving BisQue to full K8s, I started using ArgoCD for BisQue as our Continuous Deployment system and was immediately blown away by the ease of use. I was forced to be more organized and structured with my GitHub commits, which resulted in more stable releases. My previous experience with the Argo team was with Argo Workflows loved that too so now BisQue's entire module execution engine is powered by Argo Workflows.
ArgoCD offers two types of installation methods
- Quickstart install.yaml Mainly for trying out ArgoCD, small to large projects would see an immediate use case, in my opinion.
- Production HA ha/install.yaml The route to go for production
NOTE: I am assuming you have kubectl installed and you know the location of your KUBECONFIG file.
-
kubectlCLI Installed -
KUBECONFIG(default location is~/.kube/config).
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
Creates argocd namespace and installs Argo CD application. You should see the following successful deployment of the pods:
[root@amil ~]# kubectl get pods -n argocd
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
argocd-notifications-controller-5549f47758-c46f7 1/1 Running 0 31m
argocd-redis-79bdbdf78f-c42zc 1/1 Running 0 31m
argocd-applicationset-controller-79f97597cb-bxfgg 1/1 Running 1 (30m ago) 31m
argocd-dex-server-6fd8b59f5b-rzbpb 1/1 Running 0 31m
argocd-application-controller-0 1/1 Running 0 31m
argocd-repo-server-5569c7b657-k5h2f 1/1 Running 0 31m
argocd-server-664b7c6878-dh2sb 1/1 Running 0 31m
svclb-argocd-server-q6tpx 2/2 Running 0 16m
Option 1 Port-Forwarding
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443
If you are using a remote machine, remember to set the --address flag.
Example with Address Flag
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443 --address 128.112.93.8
Option 2 Service Type Load Balancer
kubectl patch svc argocd-server -n argocd -p '{"spec": {"type": "LoadBalancer"}}'
Get the Initial Password
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d; echo
You should see an output similar to fboS9Fj-sBwetVyB which is our initial password.
USERNAME: admin
PASSWORD: fboS9Fj-sBwetVyB
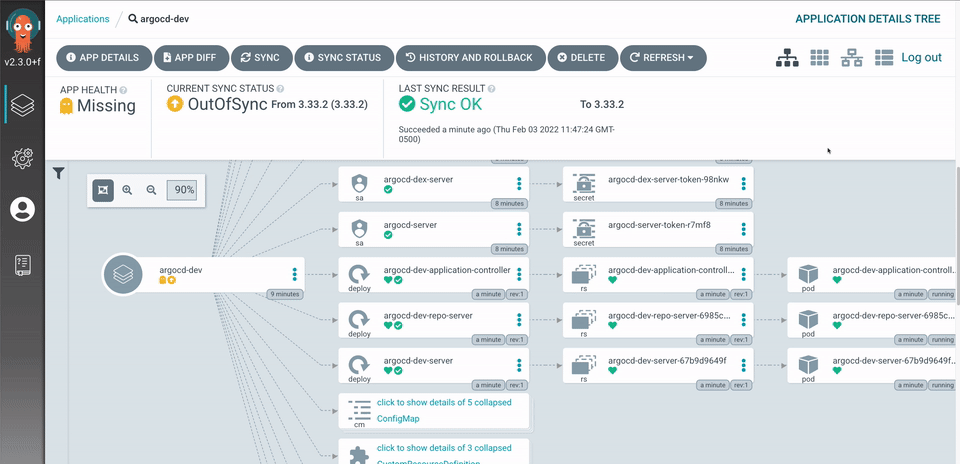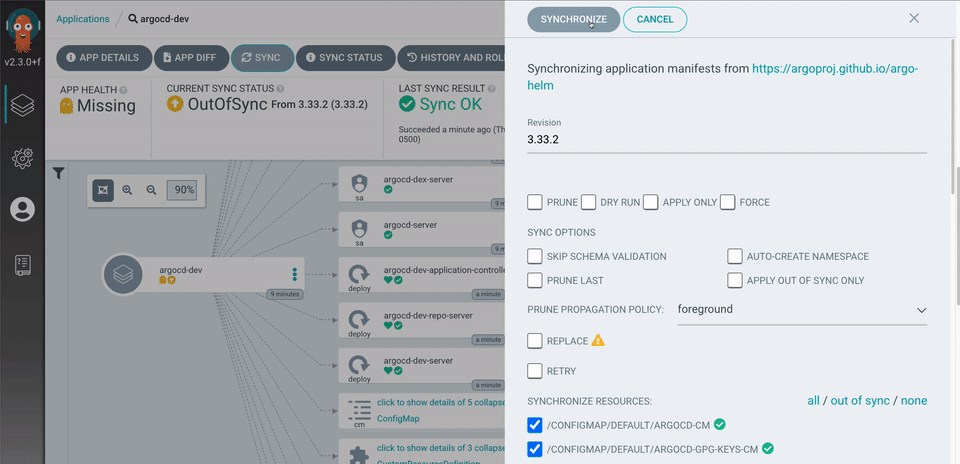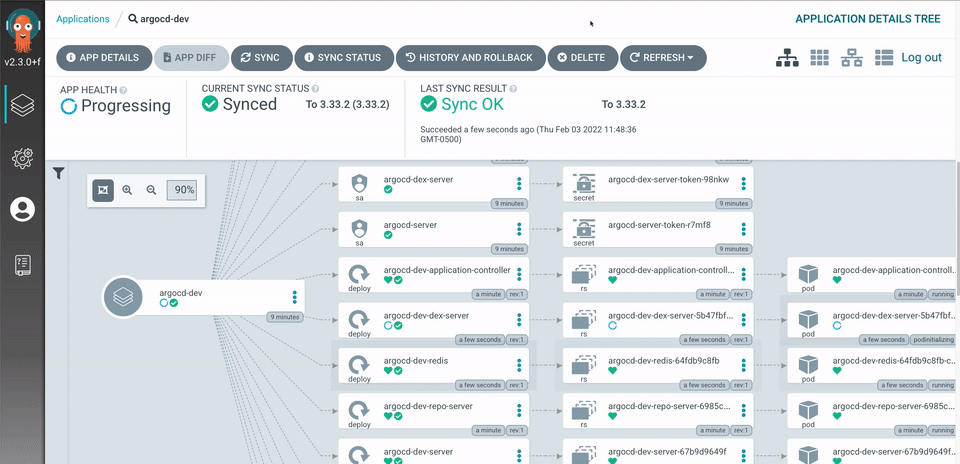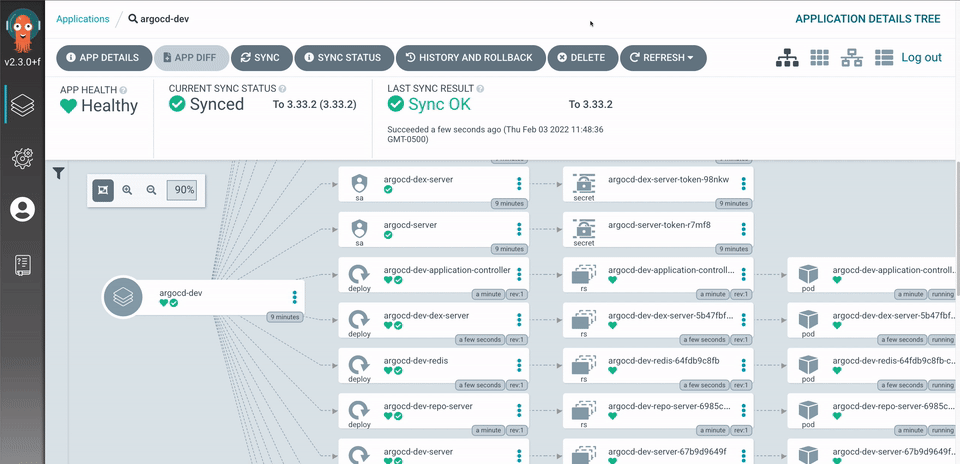
For this demonstration, I am using Argo Workflows and ArgoCD to showcase the continuous deployment and management side of ArgoCD. YES, ArgoCD managing itself!
I created a folder argo-workflows and got the quickstart-postgres.yaml for Argo Workflows into that folder. I also did the same for ArgoCD.
General Outline
- Create Github Repo
- Clone the repo locally
- Create a folder for your application deployment
argo-workflows - Go to the ArgoCD UI, Login, and select
+ NEW APP - Name your application, add the github repo, and specify the folder where your manifests live,
argo-workflows - Hit
CREATE!
mkdir argo-workflows
cd argo-workflows
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-workflows/master/manifests/quick-start-postgres.yaml
If you did not specify Automatic Sync, then you have to manually click Sync when you create the application.