The following are common problems you may face when using or developing DJL.
Please review this list before submitting an issue.
These could be due to several reasons.
16:57:55.313 [main] ERROR ai.djl.examples.training.util.AbstractTraining - Unexpected error
ai.djl.engine.EngineException: No deep learning engine found.
at ai.djl.engine.Engine.getInstance(Engine.java:81) ~[main/:?]
at ai.djl.examples.training.util.Arguments.<init>(Arguments.java:42) ~[main/:?]
at ai.djl.examples.training.util.AbstractTraining.runExample(AbstractTraining.java:67) [main/:?]
at ai.djl.examples.training.TrainPikachu.main(TrainPikachu.java:72) [main/:?]
For Windows 10 specifically, DJL many fail due to missing Visual C++ 2019 Redistributable Packages. You can install this package and reboot again to see if the issue persist. You can also check the below instruction to do further investigation.
CN: Windows 10 加载失败常常是因为缺少 Windows Visual C++ 相关扩展包而导致的。您可以通过下面Windows的步骤来修复系统缺失依赖项。
DJL currently supports four engines: MXNet, PyTorch, TensorFlow and FastText. Please include at least one of those engines and their native library as dependencies. For example, adding MXNet engine dependencies:
Gradle:
implementation "ai.djl.mxnet:mxnet-engine:0.10.0"
// See https://github.com/awslabs/djl/blob/master/mxnet/mxnet-engine/README.md for more MXNet library selection options
runtimeOnly "ai.djl.mxnet:mxnet-native-auto:1.7.0-backport"
Maven:
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.djl.mxnet</groupId>
<artifactId>mxnet-engine</artifactId>
<version>{version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<!--
See https://github.com/awslabs/djl/blob/master/mxnet/mxnet-engine/README.md for more MXNet library selection options
-->
<groupId>ai.djl.mxnet</groupId>
<artifactId>mxnet-native-auto</artifactId>
<version>{mxnet.version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
The error may appear after running the ./gradlew clean command:
This issue is caused by a mismatch between IntelliJ and the Gradle runner.
To fix this, navigate to: Preferences-> Build Execution Deployment -> Build Tools -> Gradle. Then, change the Build and running using: option to Gradle.
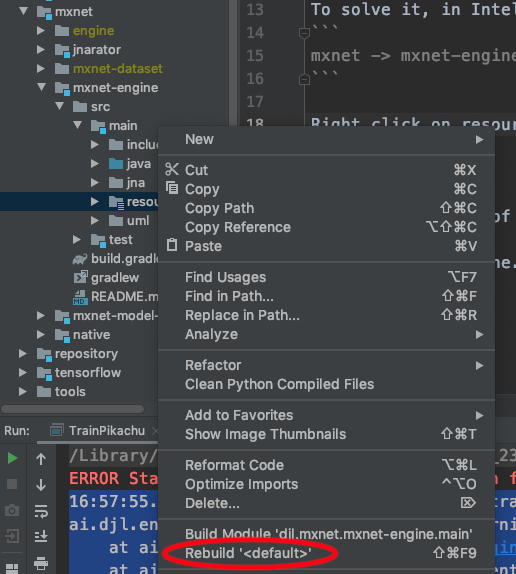
If you prefer to continue using IntelliJ IDEA as your runner, you can navigate to the MXNet engine resources folder using the project view as follows:
mxnet -> mxnet-engine -> src -> main -> resources
Then, right click the resources folder and select Rebuild<default>.
You might see the error when DJL tries to load the native library for the engines, but some shared libraries are missing.
Let's take the PyTorch engine as an example.
DJL loads libtorch.dylib when creating the Engine instance.
You can check library files on which libtorch.dylib depends by typing otool -L libtorch.dylib on mac ldd libtorch.so on ubuntu.
# in macos environment
libtorch.dylib:
@rpath/libtorch.dylib (compatibility version 0.0.0, current version 0.0.0)
@rpath/libiomp5.dylib (compatibility version 5.0.0, current version 5.0.0)
/usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1252.0.0)
@rpath/libc10.dylib (compatibility version 0.0.0, current version 0.0.0)
/usr/lib/libc++.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 400.9.0)
It shows the libtorch.dylib depends on libiomp5.dylib and libc10.dylib. If one of them is missing, it throws an UnsatisfiedLinkError exception.
If you are using ai.djl.{engine}:{engine}-native-auto, please create an issue at https://github.com/awslabs/djl.
Windows
You can run the following if you have Visual Studio tools CMD:
dumpbin /dependents your_dll_file.dllor install a Dependency Walker. It's an application that can check the dependencies for a specific DLL by simply drag and drop.
DJL requires Visual C++ Redistributable Packages. If you encounter an UnsatisfiedLinkError while building DJL on Windows, please download and install Visual C++ 2019 Redistributable Packages and reboot.
CN: 如果您在中国,可以使用 DirectX 修复工具 来安装遗失依赖项。
If the issue continues to persist, you can use the docker file provided by us. Please note that this docker will only work with Windows server 2019 by default. If you want it to work with other versions of Windows, you need to pass the version as an argument as follows:
docker build --build-arg version=<YOUR_VERSION>
Sometimes you may only have read-only access on the machine. It will cause a failure during engine loading because the cache attempts to write to the home directory. For more information, please refer to DJL Cache Management.
It happened when you had a wrong version with DJL and Deep Engines. You can check the combination here and use DJL BOM to solve the issue.
The following exception may appear after running the ./gradlew clean command:
ERROR StatusLogger No Log4j 2 configuration file found. Using default configuration (logging only errors to the console), or user programmatically provided configurations. Set system property 'log4j2.debug' to show Log4j 2 internal initialization logging. See https://logging.apache.org/log4j/2.x/manual/configuration.html for instructions on how to configure Log4j 2This issue has the same root cause as issue #1. You can follow the steps outlined previously to change Build and running using: to Gradle.
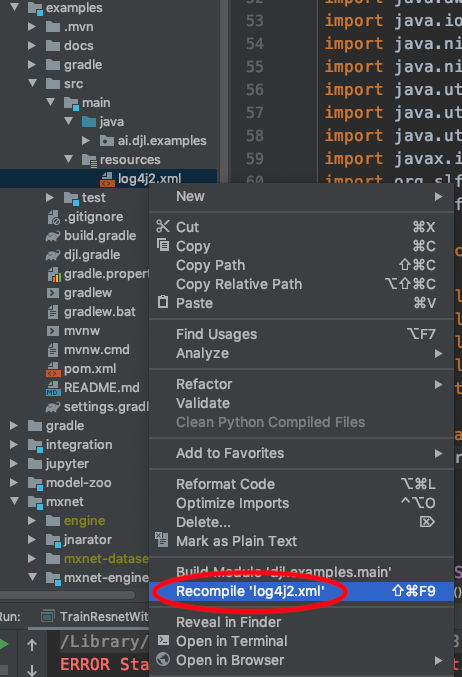
If you prefer to continue using IntelliJ IDEA as your runner, navigate to the project view for the program and recompile the log configuration file.
For example, if you are running a DJL example, navigate to:
examples -> src -> main -> resources -> log4j2.xml
Then, right click the log4j2.xml file and select Recompile log4j2.xml.
Note: this is not officially supported by DJL, and some functions may not work. If you require features in Apache MXNet not provided by DJL, please submit an issue.
By default, DJL is running on the MXNet engine.
We use mxnet-mkl on CPU machines and mxnet-cu102mkl on GPU machines.
mkl means Intel-MKLDNN is enabled.
cu102 means Nvidia CUDA Toolkit version 10.2 is enabled.
You don't need to download and install Apache MXNet separately. It's automatically done when you
build the DJL project by running the ./gradlew build command. However, you still have the option to use other versions of MXNet and to build your own customized version.
Follow the MXNet Installation guide to install other versions of MXNet.
You need the latest Apache MXNet to work with DJL, so remember to add --pre at the end of your pip install command.
After installing Apache MXNet, you need to update the MXNET_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable with your libmxnet.so file location.
For example, if you are using an older version of CUDA(version 9.2), you can install Apache MXNet with CUDA 9.2 by running the following command:
pip install mxnet-cu92 --preAfter installation, you can find the file location using the following commands in python:
python
>>> import mxnet as mx
>>> mx.__file__
'//anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/mxnet/__init__.py'Update the environment variable value with the following command:
export MXNET_LIBRARY_PATH=//anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/mxnet/Now DJL will automatically use the Apache MXNet library from this location.
Sometimes gradle may fail or get stuck. For example, you may see the following error:
* What went wrong:
Execution failed for task ':api:formatJava'.
> unable to create new native threadYou need kill the gradle daemon process:
./gradlew --stopAfter this, it should work when you re-run your command.
Running unit or integration tests manually from IntelliJ sometimes fails with the message "No tasks available".
If that happens, the following can help: Go to File > Settings > Build, Execution, Deployment > Build Tools > Gradle and change the option "Run tests using" from "Gradle" to "IntelliJ Idea".
Often, the test itself does not actually hang. To run the integration tests, the integration subproject
has a -SNAPSHOT dependency on the mxnet native binaries, ai.djl.mxnet:mxnet-native-auto. As it
is a snapshot depency, it is updated by the build system regularly. If your integration tests hang,
it is most likely just the automatic binary dependency being updated. As the total size is roughly
1.7GB the download may take a while. Once this download is over, all further tests will run instantly.
If you are using TensorFlow 2.3.1 engine with GPU and encountered the following error:
Caused by: java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: /home/ubuntu/.tensorflow/cache/2.3.1-SNAPSHOT-cu101-linux-x86_64/libjni$
ensorflow.so: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6: version `CXXABI_1.3.11' not found (required by /home/ubuntu/.te
nsorflow/cache/2.3.0-SNAPSHOT-cu101-linux-x86_64/libtensorflow.so.2)Please upgrade gcc version according to the steps on TensorFlow install page
When you run object detection using Jupyter Notebooks on EC2 instances via SSH, sometimes you may face X11 error when drawing bounding boxes.
java.awt.HeadlessException:
No X11 DISPLAY variable was set, but this program performed an operation which requires it.
java.awt.HeadlessException:Follow the steps here to resolve it.
It is very unfortunate to have issue since the error logging is not very clear. There are many causes that can trigger this issue. If you have issues debugging, please file us an issue on GitHub or on Slack and we can check with you. Here is a summary on the issues we have dealt before.
Sometimes the OOM issue will trigger the Core Dump error message.
It can be the heap memory overflow and cause a chain of failure from native memory to Java.
Try to increase the xmx may help to reduce this issue,
you can also try to monitor the heap memory cost to identify if this is the root cause.
This issue is fairly common in the Multithreaded Inference/Training cases and will trigger the segfault or Core Dump error message.
The Java GC has kicked in and release some of the pointers beforehand. Generally, you may need to disable the GC happened in this case
and relying on DJL's NDManager to efficiently GC the memory. You can do that by adding flag
-Dai.djl.disable_close_resource_on_finalize=true