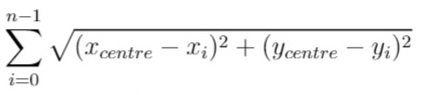A delivery company wants to build a new service centre in a new city. The company knows the positions of all the customers in this city on a 2D-Map and wants to build the new centre in a position such that the sum of the euclidean distances to all customers is minimum.
Given an array positions where positions[i] = [xi, yi] is the position of the ith customer on the map, return the minimum sum of the euclidean distances to all customers.
In other words, you need to choose the position of the service centre [xcentre, ycentre] such that the following formula is minimized:
Answers within 10^-5 of the actual value will be accepted.
Example 1:
Input: positions = [[0,1],[1,0],[1,2],[2,1]] Output: 4.00000 Explanation: As shown, you can see that choosing [xcentre, ycentre] = [1, 1] will make the distance to each customer = 1, the sum of all distances is 4 which is the minimum possible we can achieve.
Example 2:
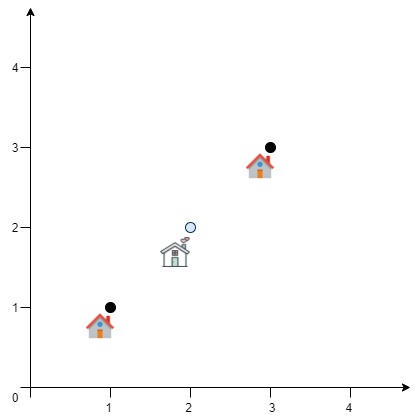
Input: positions = [[1,1],[3,3]] Output: 2.82843 Explanation: The minimum possible sum of distances = sqrt(2) + sqrt(2) = 2.82843
Example 3:
Input: positions = [[1,1]] Output: 0.00000
Example 4:
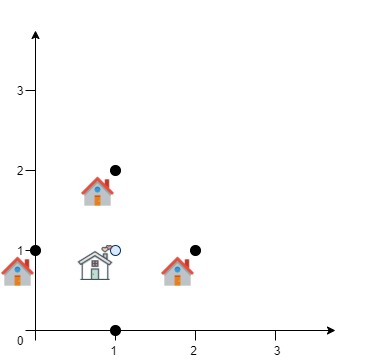
Input: positions = [[1,1],[0,0],[2,0]] Output: 2.73205 Explanation: At the first glance, you may think that locating the centre at [1, 0] will achieve the minimum sum, but locating it at [1, 0] will make the sum of distances = 3. Try to locate the centre at [1.0, 0.5773502711] you will see that the sum of distances is 2.73205. Be careful with the precision!
Example 5:
Input: positions = [[0,1],[3,2],[4,5],[7,6],[8,9],[11,1],[2,12]] Output: 32.94036 Explanation: You can use [4.3460852395, 4.9813795505] as the position of the centre.
Constraints:
1 <= positions.length <= 50positions[i].length == 20 <= positions[i][0], positions[i][1] <= 100
Related Topics:
Geometry
Starting from a random point (here I use (0, 0)). We move around in 4 directions with some initial step (I used 100).
If we can find smaller total distance, we move to that point.
Otherwise, we set step /= 2.
We keep this iteration until the step is smaller than 1e-6.
See more:
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12934213/how-to-find-out-geometric-median
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geometric_median
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/best-position-for-a-service-centre/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N * S) where S is the steps taken to reach the center
// Space: O(1)
class Solution {
double dist(vector<int> &a, vector<double> &b) {
return sqrt(pow(a[0] - b[0], 2) + pow(a[1] - b[1], 2));
}
double all(vector<vector<int>> &A, vector<double> &p) {
double ans = 0;
for (auto &a : A) ans += dist(a, p);
return ans;
}
const int dirs[4][2] = {{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0},{1,0}};
public:
double getMinDistSum(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
double ans = DBL_MAX, step = 100, eps = 1e-6;
vector<double> p(2, 0);
while (step > eps) {
bool found = false;
for (auto &dir : dirs) {
vector<double> next = {p[0] + step * dir[0], p[1] + step * dir[1]};
double d = all(A, next);
if (d < ans) {
ans = d;
p = next;
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found) step /= 2;
}
return ans;
}
};