A frontend Framework for building admin applications on top of REST services, using ES6, React and Material UI.
Admin-on-rest is available from npm.
npm install --save-dev admin-on-restRead the docs/Tutorial.md for a presentation of admin-on-rest usage.
// in app.js
import React from 'react';
import { render } from 'react-dom';
import { simpleRestClient, Admin, Resource } from 'admin-on-rest';
import { PostList, PostEdit, PostCreate, PostIcon } from './posts';
render(
<Admin restClient={simpleRestClient('http://localhost:3000')}>
<Resource name="posts" list={PostList} edit={PostEdit} create={PostCreate} icon={PostIcon}/>
</Admin>,
document.getElementById('root')
);The <Resource> component is a configuration component that allows to define sub components for each of the admin view: list, edit, and create. These components use Material UI and custom components from admin-on-rest:
// in posts.js
import React from 'react';
import { List, Edit, Create, Datagrid, DateField, TextField, EditButton, DisabledInput, TextInput, LongTextInput, DateInput } from 'admin-on-rest/lib/mui';
export PostIcon from 'material-ui/svg-icons/action/book';
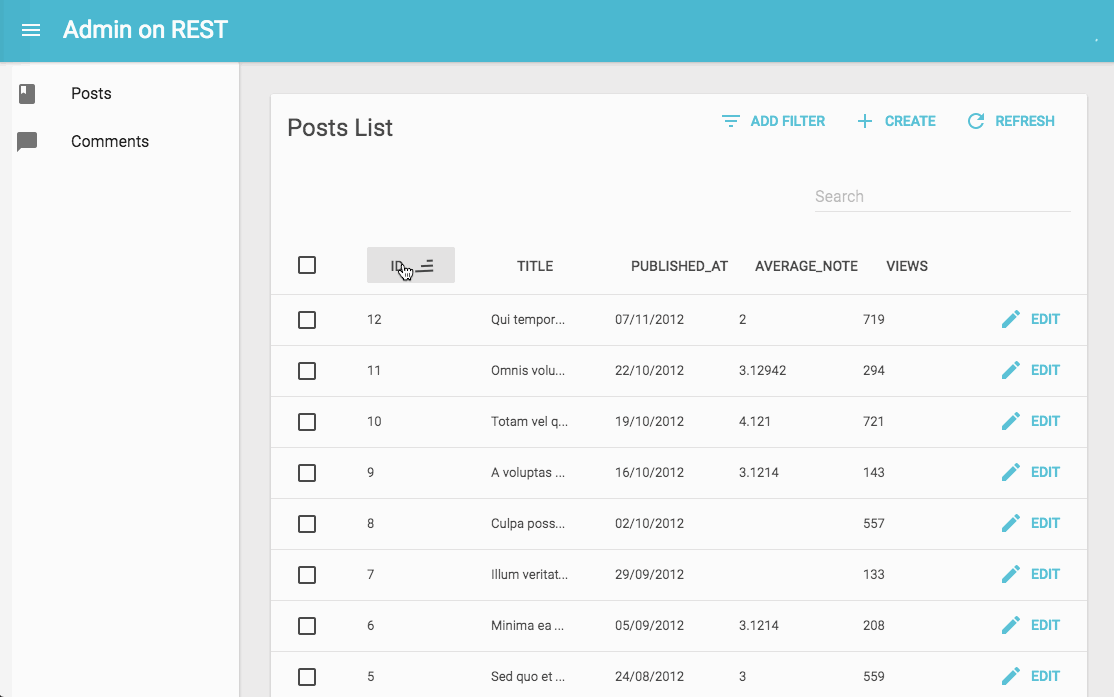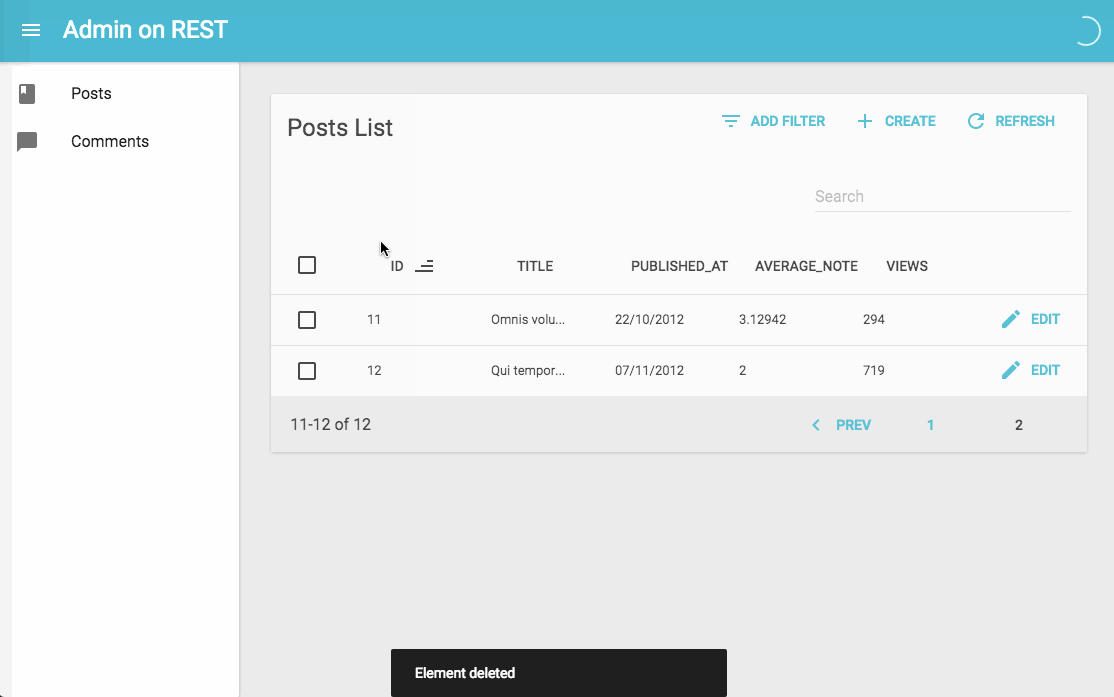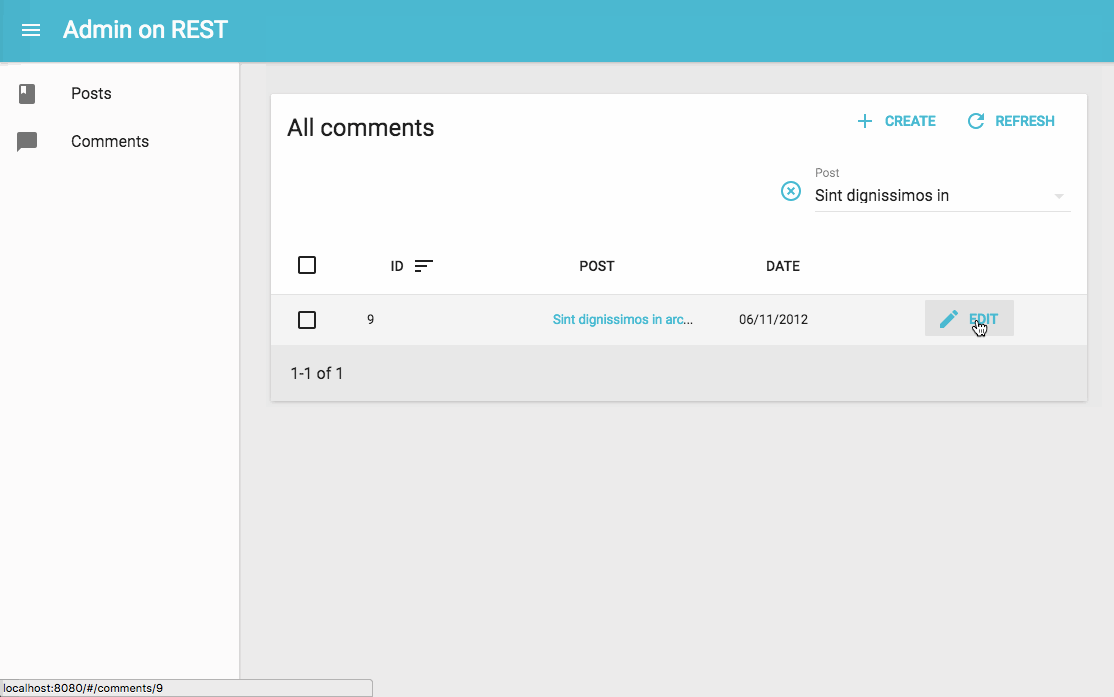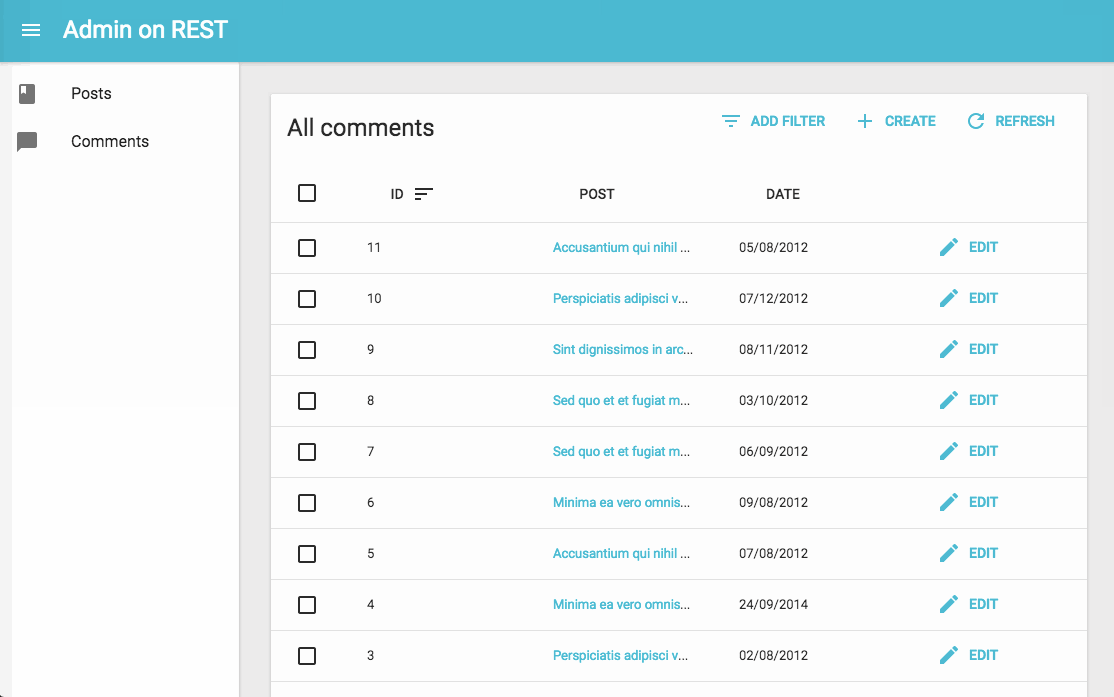
export const PostList = (props) => (
<List {...props}>
<Datagrid>
<TextField label="id" source="id" />
<TextField label="title" source="title" />
<DateField label="published_at" source="published_at" />
<TextField label="average_note" source="average_note" />
<TextField label="views" source="views" />
<EditButton basePath="/posts" />
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
const PostTitle = ({ record }) => {
return <span>Post {record ? `"${record.title}"` : ''}</span>;
};
export const PostEdit = (props) => (
<Edit title={PostTitle} {...props}>
<DisabledInput label="Id" source="id" />
<TextInput label="Title" source="title" />
<TextInput label="Teaser" source="teaser" options={{ multiLine: true }} />
<LongTextInput label="Body" source="body" />
<DateInput label="Publication date" source="published_at" />
<TextInput label="Average note" source="average_note" />
<DisabledInput label="Nb views" source="views" />
</Edit>
);
export const PostCreate = (props) => (
<Create title="Create a Post" {...props}>
<TextInput label="Title" source="title" />
<TextInput label="Teaser" source="teaser" options={{ multiLine: true }} />
<LongTextInput label="Body" source="body" />
<TextInput label="Publication date" source="published_at" />
<TextInput label="Average note" source="average_note" />
</Create>
);REST isn't a standard, so it's impossible to make a REST client library that will work for all REST backends. Admin-on-rest deals with this problem by letting you provide a REST client function. This is the place to translate REST requests to HTTP requests, and HTTP responses to REST responses.
The <Admin> component expects a restClient parameter, which is a function with the following signature:
/**
* Execute the REST request and return a promise for a REST response
*
* @example
* restClient(GET_ONE, 'posts', { id: 123 })
* => new Promise(resolve => resolve({ data: { id: 123, title: "hello, world" } }))
*
* @param {string} type Request type, e.g GET_LIST
* @param {string} resource Resource name, e.g. "posts"
* @param {Object} payload Request parameters. Depends on the action type
* @returns {Promise} the Promise for a REST response
*/
const restClient = (type, resource, params) => new Promise();The expected format for REST requests and responses is documented in src/rest/README.md; you can find an example in src/rest/simple.js;
The restClient is also the ideal place to add custom HTTP headers, authentication, etc.
Although it's fast and easy to build an admin using the <Admin> and <Resource> components, it is also possible to include the admin logic into an existing React application. You are strongly encouraged to use the lower-level elements or admin-to-rest, provided you're familiar with Redux, react-router and redux-saga.
The library makes no assumption on the side effect library you want to use, but provides examples for redux-saga.
The side effects expected by admin-on-rest are AJAX calls to the REST backend(s), and redirects. They must respond to the following actions:
- CRUD_GET_LIST => CRUD_GET_LIST_SUCCESS
- CRUD_GET_ONE => CRUD_GET_ONE_SUCCESS
- CRUD_UPDATE => CRUD_UPDATE_SUCCESS
- CRUD_CREATE => CRUD_CREATE_SUCCESS
- CRUD_DELETE => CRUD_DELETE_SUCCESS
Check sideEffect/saga.js for a detail of the inputs and outputs
- Add more documentation
- Improve error handling
- Form validation
- Add unit tests
- Add
<ReferenceMany>field - Add complex field & input types