-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Cindy
Cindy is a student and she has heard from her friends about the possibility to setup a stake pool with Cardano Shelley. She would like to try this out. She needs to follow the steps like Frank did.


Step 1: Debian/Ubuntu
Prepare a machine with the operating system Debian or Ubuntu.
Step 2: Install packages
Install the next packages:
$ sudo apt-get update -y
$ sudo apt-get -y install build-essential pkg-config libffi-dev libgmp-dev libssl-dev libtinfo-dev libsystemd-dev zlib1g-dev make g++ tmux git jq wget libncursesw5
Step 3: Download, unpack, install and update Cabal
Install Cabal
$ wget https://downloads.haskell.org/~cabal/cabal-install-3.2.0.0/cabal-install-3.2.0.0-x86_64-unknown-linux.tar.xz
$ tar -xf cabal-install-3.2.0.0-x86_64-unknown-linux.tar.xz
$ rm cabal-install-3.2.0.0-x86_64-unknown-linux.tar.xz cabal.sig
$ mkdir -p ~/.local/bin
$ mv cabal ~/.local/bin/
Add PATH to .bashrc-file
export PATH="~/.cabal/bin:$PATH"
export PATH="~/.local/bin:$PATH"
Update cabal
$ source .bashrc
$ cabal update
Install GHC
$ wget https://downloads.haskell.org/~ghc/8.6.5/ghc-8.6.5-x86_64-deb9-linux.tar.xz
$ tar -xf ghc-8.6.5-x86_64-deb9-linux.tar.xz
$ rm ghc-8.6.5-x86_64-deb9-linux.tar.xz
$ cd ghc-8.6.5
$ ./configure
$ sudo make install
$ cd ..
Install Libsodium
$ git clone https://github.com/input-output-hk/libsodium
$ cd libsodium
$ git checkout 66f017f1
$ ./autogen.sh
$ ./configure
$ make
$ sudo make install
$ cd ..$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/usr/local/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH"Step 4: Download the source code for cardano-node
$ git clone https://github.com/input-output-hk/cardano-node.git
$ cd cardano-node
$ git fetch --all --tags
Step 5: Build and install the node
First build
Replace <the-tag-you-want> with the tag that you want to retrieve and build the codes.
$ git checkout tags/<the-tag-you-want>
Add overwrite-policy: alwaysin .cabal/config-file
$ cabal install cardano-node cardano-cli
Next fetch and build
Retrieve the latest codes
$ cd cardano-node
$ git fetch --all --tags
$ git tag
$ git checkout tags/<the-tag-you-want>
$ cabal install cardano-node cardano-cli
Step 6: Copy executable files
Copy the executable files to the host servers.
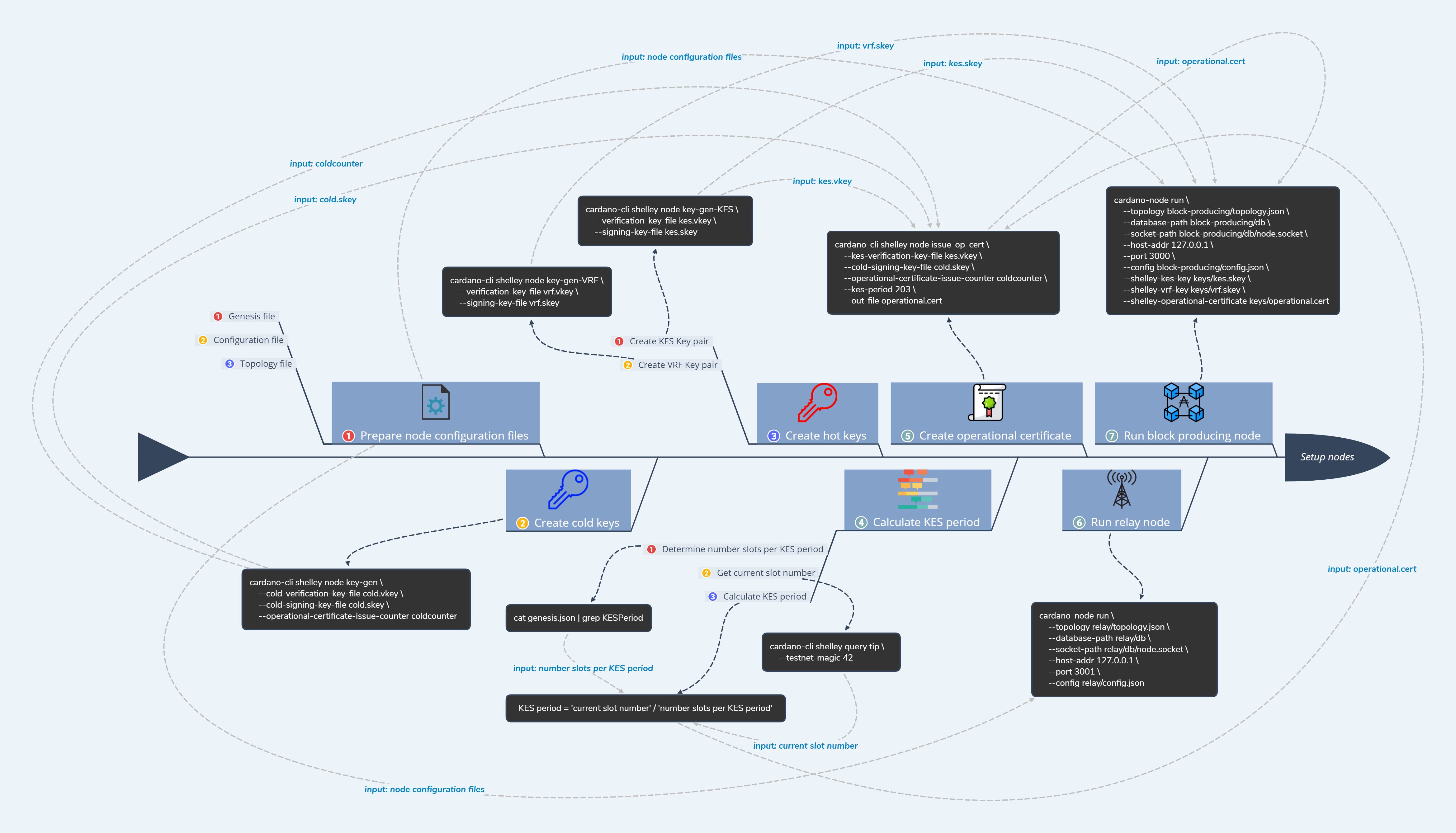
Cindy has planned to have the next configuration for her nodes:

Step 1: Prepare node configuration files
Create the next directories in the working directory:
mkdir configuration
mkdir relay
mkdir block-oneDownload genesis, configuration and topology files from https://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/cardano-node/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/index.html
wget -O configuration/topology.json https://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/cardano-node/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/shelley_testnet-topology.json
wget -O configuration/genesis.json https://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/cardano-node/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/shelley_testnet-genesis.json
wget -O configuration/config.json https://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/cardano-node/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/shelley_testnet-config.jsonRun the next command to update the config.json file, because we have renamed shelley_testnet-genesis.json to genesis.json.
sed -i 's/shelley_testnet-genesis.json/genesis.json/g' configuration/config.jsonCopy the configuration files to relay, block-one and block-two:
cp -avr configuration/ relay/
cp -avr configuration/ block-one/She makes the next modification in relay/configuration/topology.json:
{
"Producers": [
{
"addr": "relays-new.shelley-testnet.dev.cardano.org",
"port": 3001,
"valency": 2
},
{
"addr": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 7510,
"valency": 1
}
]
}
And in block-one/configuration/topology.json:
{
"Producers": [
{
"addr": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 7500,
"valency": 1
}
]
}
Step 2: Run relay node
The relay node is now ready and can be started:
cardano-node run \
--topology relay/configuration/topology.json \
--database-path relay/db \
--socket-path relay/db/node.socket \
--host-addr 0.0.0.0 \
--port 7500 \
--config relay/configuration/config.jsonStep 3: Create cold keys
Create a new subdirectory keys under block-one:
mkdir block-one/keysRun the next command to create the cold keys for block-one:
cardano-cli shelley node key-gen \
--cold-verification-key-file block-one/keys/cold.vkey \
--cold-signing-key-file block-one/keys/cold.skey \
--operational-certificate-issue-counter block-one/keys/coldcounterStep 4: Create hot keys
Run the next command to create the hot keys for block-one:
cardano-cli shelley node key-gen-KES \
--verification-key-file block-one/keys/kes.vkey \
--signing-key-file block-one/keys/kes.skey
cardano-cli shelley node key-gen-VRF \
--verification-key-file block-one/keys/vrf.vkey \
--signing-key-file block-one/keys/vrf.skeyHer folder structure looks like this now:

Step 5: Create operational certificates
Determine the number slots per KES period:
cat relay/configuration/genesis.json | grep KESPeriodResult:
"slotsPerKESPeriod": 3600,Next check the current slot number:
export CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH=relay/db/node.socketcardano-cli shelley query tip \
--testnet-magic 42Result:
Tip (SlotNo {unSlotNo = 483680}) (ShelleyHash {unShelleyHash = HashHeader {unHashHeader = 4397c421aec9e3efe23a94e03b1a92c49f3d697dd987d4eb5a5c27832fbde8ea}}) (BlockNo {unBlockNo = 22551})Calculate the KES period:
expr 483680 / 3600Result is 134.
Create the operational certificate:
cardano-cli shelley node issue-op-cert \
--kes-verification-key-file block-one/keys/kes.vkey \
--cold-signing-key-file block-one/keys/cold.skey \
--operational-certificate-issue-counter block-one/keys/coldcounter \
--kes-period 134 \
--out-file block-one/keys/operational.certoperational.cert-files contain the operational certificates.
Step 6: Run block producing nodes with the operational keys and certificates
cardano-node run \
--topology block-one/configuration/topology.json \
--database-path block-one/db \
--socket-path block-one/db/node.socket \
--host-addr 127.0.0.1 \
--port 7510 \
--config block-one/configuration/config.json \
--shelley-kes-key block-one/keys/kes.skey \
--shelley-vrf-key block-one/keys/vrf.skey \
--shelley-operational-certificate block-one/keys/operational.certCreate the addresses directory in the next directories:
mkdir block-one/addressesAnd follow the next steps to create a new stake & payment account:

Step 1: create new payment key
cardano-cli shelley address key-gen \
--verification-key-file block-one/addresses/payment1.vkey \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/payment1.skeyStep 2: create new stake key
cardano-cli shelley stake-address key-gen \
--verification-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.vkey \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.skeyStep 3: create payment address with payment key and stake key
The payment address can be used to transfer funds.
cardano-cli shelley address build \
--payment-verification-key-file block-one/addresses/payment1.vkey \
--stake-verification-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.vkey \
--out-file block-one/addresses/payment1.addr \
--testnet-magic 42Step 4: create stake address with stake key
The stake address will be used to collect the delegation rewards.
cardano-cli shelley stake-address build \
--staking-verification-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.vkey \
--out-file block-one/addresses/stake1.addr \
--testnet-magic 42Step 5: check funds in the payment address
Set environment variable CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH to the socket-path specified in the node configuration. For example:
export CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH=relay/db/node.socketCheck funds with the next command
cardano-cli shelley query utxo \
--address $(cat block-one/addresses/payment1.addr) \
--testnet-magic 42Example result:
TxHash TxIx Lovelace
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ba354621f4268684a31bf5f0b90031567c952d727a057153aac39a7eaafec5d0 0 10000000000

Step 1: get the protocol parameters
Get the protocol parameters if not done yet.
cardano-cli shelley query protocol-parameters \
--testnet-magic 42 \
--out-file configuration/protocol.jsonStep 2: create a stake certificate
cardano-cli shelley stake-address registration-certificate \
--staking-verification-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.vkey \
--out-file block-one/addresses/stake1.certStep 3: retrieve the UTXO details from the payment address
export CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH=relay/db/node.socketRetrieve the UTXO details from the payment1.addr address of block-one.
cardano-cli shelley query utxo \
--address $(cat block-one/addresses/payment1.addr) \
--testnet-magic 42Example result:
TxHash TxIx Lovelace
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ba354621f4268684a31bf5f0b90031567c952d727a057153aac39a7eaafec5d0 0 10000000000
Step 4: determine the appropiate TTL (Time to live)
cardano-cli shelley query tip \
--testnet-magic 42Example result:
Tip (SlotNo {unSlotNo = 581365}) (ShelleyHash {unShelleyHash = HashHeader {unHashHeader = 782cb7383827f5c10555735bb173d52c0f9699d49ed536136662e79f5829bca1}}) (BlockNo {unBlockNo = 27484})Extract the current slot number unSlotNo, which is 581365 in this example. And increase it with 2000.
--ttl is:
581365 + 2000 = 583365
Step 5: calculate the fee
cardano-cli shelley transaction calculate-min-fee \
--tx-in-count 1 \
--tx-out-count 1 \
--ttl 583365 \
--testnet-magic 42 \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/payment1.skey \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.skey \
--certificate block-one/addresses/stake1.cert \
--protocol-params-file configuration/protocol.jsonExample result:
runTxCalculateMinFee: 171133Which means that we need to pay a transaction fee --fee of 171133 Lovelace.
Retrieve the registration fee for our stake certificate:
cat configuration/genesis.json | grep keyDeposit"keyDeposit": 400000,
Step 6: select UTXO and calculate the remainder funds
For block-one we will use the UTXO ba354621f4268684a31bf5f0b90031567c952d727a057153aac39a7eaafec5d0 to pay the transaction fee:
TxHash TxIx Lovelace
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ba354621f4268684a31bf5f0b90031567c952d727a057153aac39a7eaafec5d0 0 10000000000
...
--tx-in is:
--tx-in ba354621f4268684a31bf5f0b90031567c952d727a057153aac39a7eaafec5d0#0--tx-out is the remainder funds, which need to be sent back to the sender payment address. Therefore we need to calculate the change first: current total funds - registration fee - transfer fee.
10000000000 - 400000 - 171133 = 9999428867Thus --tx-out can be constructed like this:
--tx-out $(cat block-one/addresses/payment1.addr)+9999428867Step 7: build the transaction Now we have all required input parameters to build the transaction.
cardano-cli shelley transaction build-raw \
--tx-in ba354621f4268684a31bf5f0b90031567c952d727a057153aac39a7eaafec5d0#0 \
--tx-out $(cat block-one/addresses/payment1.addr)+9999428867 \
--ttl 583365 \
--fee 171133 \
--out-file block-one/transactions/tx1.txbody \
--certificate block-one/addresses/stake1.certtx1.txbody contains the output raw file.
Step 8: sign the transaction
We use the sender key pay.skey and stake.skey to sign the transaction file tx1.txbody.
cardano-cli shelley transaction sign \
--tx-body-file block-one/transactions/tx1.txbody \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/payment1.skey \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.skey \
--testnet-magic 42 \
--tx-file block-one/transactions/tx1.signedtx1.signed contains the signed transaction file.
Step 9: submit the transaction
We submit the signed transaction file tx1.signed.
cardano-cli shelley transaction submit \
--tx-file block-one/transactions/tx1.signed \
--testnet-magic 42
Step 1: get the protocol parameters
This is an optional step. Get the protocol parameters if not done yet.
cardano-cli shelley query protocol-parameters \
--testnet-magic 42 \
--out-file configuration/protocol.jsonStep 2: create a registration certificate for our stake pool
Create two JSON files which store the pool's metadata and upload to a web folder. Once done, then download them to the host servers.
mkdir block-one/pool
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ItFlyingStart/shelley-cli-overview/master/pools/Cindy_pool_1.json -P ./block-one/pool/Create the hash for these pool's metadata files:
cardano-cli shelley stake-pool metadata-hash \
--pool-metadata-file block-one/pool/Cindy_pool_1.json \
> block-one/pool/Cindy_pool_1_hashCreate a shortened version of URL, for example: with https://cutt.ly/. Use the shortened URL for the follow-up CLI command.
| Full URL to JSON metadata file | Shortened URL |
|---|---|
| https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ItFlyingStart/shelley-cli-overview/master/pools/Cindy_pool_1.json | https://cutt.ly/9oIHXkd |
Create the certificate for both stake pools. The input parameters are:
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
| stake-pool-verification-key-file | verification cold key |
| vrf-verification-key-file | verification VRS key |
| pool-pledge | pledge (lovelace) |
| pool-cost | operational costs per epoch (lovelace) |
| pool-margin | operator margin |
| pool-reward-account-verification-key-file | verification staking key for the rewards |
| pool-owner-staking-verification-key-file | verification staking key(s) for the pool owner(s) |
| out-file | output file to write the certificate to |
| pool-relay-port | port |
| pool-relay-ipv4 | relay node ip address |
| metadata-url | url of your json file |
| metadata-hash | the hash of pools json metadata file |
Example registration certificate:
cardano-cli shelley stake-pool registration-certificate \
--cold-verification-key-file block-one/keys/cold.vkey \
--vrf-verification-key-file block-one/keys/vrf.vkey \
--pool-pledge 5000000000 \
--pool-cost 90000000 \
--pool-margin 0.04 \
--pool-reward-account-verification-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.vkey \
--pool-owner-staking-verification-key block-one/addresses/stake1.vkey \
--testnet-magic 42 \
--metadata-url https://cutt.ly/9oIHXkd \
--metadata-hash $(cat block-one/pool/Cindy_pool_1_hash) \
--out-file block-one/addresses/pool.certSo in the example above, we use the cold- and VRF-keys that we have created when configuring the nodes, promise to pledge 5.000 ADA to our pool block-one, declare operational costs of 90 ADA per epoch for block-one, set the operational margin (i.e. the ratio of rewards we take after taking our costs and before the rest is distributed amongst owners and delegators according to their delegated stake) to 4% for block-one, use the staking key we created the previous chapter to receive our rewards and use the same key as pool owner key for the pledge.
Step 3: pledge stake to our stake pool
cardano-cli shelley stake-address delegation-certificate \
--staking-verification-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.vkey \
--stake-pool-verification-key-file block-one/keys/cold.vkey \
--out-file block-one/addresses/delegation.certStep 4: retrieve the UTXO details from the payment address
export CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH=relay/db/node.socketRetrieve the UTXO details from the payment1.addr address of block-one.
cardano-cli shelley query utxo \
--address $(cat block-one/addresses/payment1.addr) \
--testnet-magic 42Example result:
TxHash TxIx Lovelace
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
25c5c62108b92ee55381dfd6d60dc74688497c4be6527cb0617fd90e7e22dccf 0 9999428867
Step 5: determine the appropiate TTL (Time to live)
cardano-cli shelley query tip \
--testnet-magic 42Example result:
Tip (SlotNo {unSlotNo = 582000}) (ShelleyHash {unShelleyHash = HashHeader {unHashHeader = 2e0f9a5ce096a09883e52644a468a65593654ef5746f76e80fc17046af4b180e}}) (BlockNo {unBlockNo = 27511})Extract the current slot number unSlotNo, which is 582000 in this example. And increase it with 2000.
--ttl is:
582000 + 2000 = 584000
Step 6: calculate the fee
cardano-cli shelley transaction calculate-min-fee \
--tx-in-count 1 \
--tx-out-count 1 \
--ttl 584000 \
--testnet-magic 42 \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/payment1.skey \
--signing-key-file block-one/keys/cold.skey \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.skey \
--certificate block-one/addresses/pool.cert \
--certificate block-one/addresses/delegation.cert \
--protocol-params-file configuration/protocol.jsonExample result:
runTxCalculateMinFee: 186709Which means that we need to pay a transaction fee --fee of 186709 Lovelace.
Retrieve the registration fee for our stake pool:
cat configuration/genesis.json | grep poolDeposit"poolDeposit": 500000000,
Step 7: select UTXO and calculate the remainder funds
Block-one
We will use the UTXO 25c5c62108b92ee55381dfd6d60dc74688497c4be6527cb0617fd90e7e22dccf to pay the transaction fee and the registration fee:
TxHash TxIx Lovelace
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
25c5c62108b92ee55381dfd6d60dc74688497c4be6527cb0617fd90e7e22dccf 0 9999428867
--tx-in is:
--tx-in 25c5c62108b92ee55381dfd6d60dc74688497c4be6527cb0617fd90e7e22dccf#0--tx-out is the remainder funds, which need to be sent back to the sender payment address. Therefore we need to calculate the change first: current total funds - registration fee - transfer fee.
9999428867 - 500000000 - 186709 = 9499242158Thus --tx-out can be constructed like this:
--tx-out $(cat block-one/addresses/payment1.addr)+9499242158Step 8: build the transaction Now we have all required input parameters to build the transaction.
cardano-cli shelley transaction build-raw \
--tx-in 25c5c62108b92ee55381dfd6d60dc74688497c4be6527cb0617fd90e7e22dccf#0 \
--tx-out $(cat block-one/addresses/payment1.addr)+9499242158 \
--ttl 584000 \
--fee 186709 \
--tx-body-file block-one/transactions/tx1.txbody \
--certificate block-one/addresses/pool.cert \
--certificate block-one/addresses/delegation.certtx1.txbody contains the output raw file.
Step 9: sign the transaction
We use the sender key payment1.skey, cold.skey and stake1.skey to sign the transaction file tx1.txbody.
cardano-cli shelley transaction sign \
--tx-body-file block-one/transactions/tx1.txbody \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/payment1.skey \
--signing-key-file block-one/keys/cold.skey \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/stake1.skey \
--testnet-magic 42 \
--tx-file block-one/transactions/tx1.signedtx1.signed contains the signed transaction file.
Step 10: submit the transaction
We submit the signed transaction file tx1.signed.
cardano-cli shelley transaction submit \
--tx-file block-one/transactions/tx1.signed \
--testnet-magic 42
Determine the pool ID:
cardano-cli shelley stake-pool id \
--verification-key-file block-one/keys/cold.vkey \
> block-one/keys/stake-pool.idCheck for the presence of our pool ID of block-one in the network ledger state (or using https://pooltool.io/):
cardano-cli shelley query ledger-state --testnet-magic 42 | grep poolPubKey | grep $(cat block-one/keys/stake-pool.id) "_poolPubKey": "82093603b88f18cc7c14c157a674c9da7f80946bb7faab1140d9e615339938d3",Unfortunately Cindy doesn't have enough time to maintain her stake pool. Therefore she has decided to deregrister her stake pool.
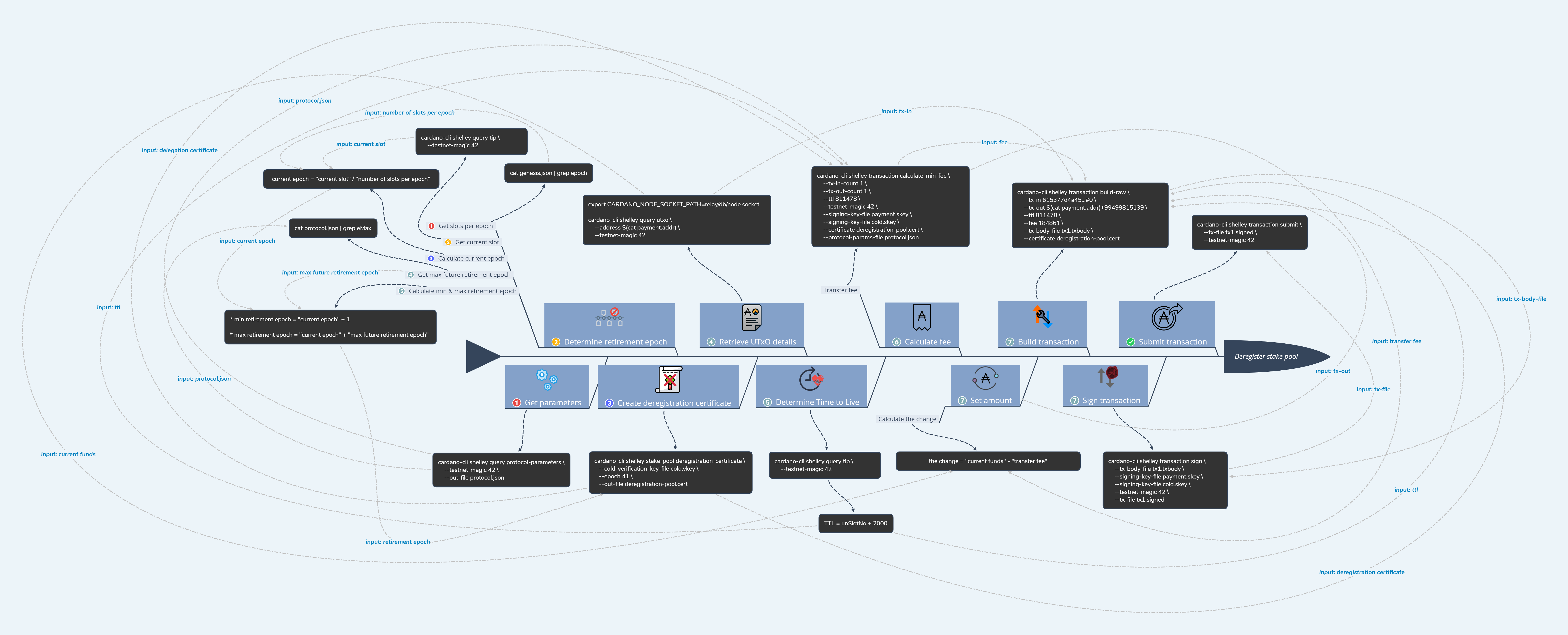
Step 1: get the protocol parameters
This is an optional step. Get the protocol parameters if not done yet.
cardano-cli shelley query protocol-parameters \
--testnet-magic 42 \
--out-file configuration/protocol.jsonStep 2: determine retirement epoch
Get the number of slots per epoch:
cat configuration/genesis.json | grep epoch "epochLength": 21600,Get the current slot by querying the tip:
cardano-cli shelley query tip \
--testnet-magic 42Example result:
Tip (SlotNo {unSlotNo = 583225}) (ShelleyHash {unShelleyHash = HashHeader {unHashHeader = 14fe98381d71cc138f15c49b49015a118520ff7826f760bf03f187d4d0f976ff}}) (BlockNo {unBlockNo = 27570})Extract the current slot number unSlotNo, which is 583225 in this example.
Calculate the current epoch:
expr 583225 / 21600Which is the epoch 27.
Look up the max future retirement epoch eMax by querying the current protocol parameters:
cat configuration/protocol.json | grep eMax "eMax": 18,This means the earliest epoch for retirement is 28 (one in the future), and the latest is 45 (current epoch plus eMax).
Step 3: create deregistration certificate for our stake pool
cardano-cli shelley stake-pool deregistration-certificate \
--cold-verification-key-file block-one/keys/cold.vkey \
--epoch 28 \
--out-file block-one/addresses/pool-deregistration.certStep 4: retrieve the UTXO details from the payment address
export CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH=relay/db/node.socketRetrieve the UTXO details from the payment1.addr address of block-one.
cardano-cli shelley query utxo \
--address $(cat block-one/addresses/payment1.addr) \
--testnet-magic 42Example result:
TxHash TxIx Lovelace
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
130f907864baccf1b12d9a310bdab94a524bf3c8feb185b353385d7dedd9c7a0 0 9499242158
Step 5: determine the appropiate TTL (Time to live)
cardano-cli shelley query tip \
--testnet-magic 42Example result:
Tip (SlotNo {unSlotNo = 583807}) (ShelleyHash {unShelleyHash = HashHeader {unHashHeader = 9a3c4df61d6f0dce9940ac17f7b84dd6d36bc9e5e290d1bf0d114a482e436ad0}}) (BlockNo {unBlockNo = 27601})Extract the current slot number unSlotNo, which is 583807 in this example. And increase it with 2000.
--ttl is:
583807 + 2000 = 585807
Step 6: calculate the fee
cardano-cli shelley transaction calculate-min-fee \
--tx-in-count 1 \
--tx-out-count 1 \
--ttl 585807 \
--testnet-magic 42 \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/payment1.skey \
--signing-key-file block-one/keys/cold.skey \
--certificate block-one/addresses/pool-deregistration.cert \
--protocol-params-file configuration/protocol.jsonExample result:
runTxCalculateMinFee: 171133Which means that we need to pay a transaction fee --fee of 171133 Lovelace.
Step 7: select UTXO and calculate the remainder funds
We will use the UTXO 130f907864baccf1b12d9a310bdab94a524bf3c8feb185b353385d7dedd9c7a0 to pay the transaction fee and the registration fee:
TxHash TxIx Lovelace
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
130f907864baccf1b12d9a310bdab94a524bf3c8feb185b353385d7dedd9c7a0 0 9499242158
--tx-in is:
--tx-in 130f907864baccf1b12d9a310bdab94a524bf3c8feb185b353385d7dedd9c7a0#0--tx-out is the remainder funds, which need to be sent back to the sender payment address. Therefore we need to calculate the change first: current total funds - transfer fee.
9499242158 - 171133 = 9499071025Thus --tx-out can be constructed like this:
--tx-out $(cat block-one/addresses/payment1.addr)+9499071025Step 8: build the transaction Now we have all required input parameters to build the transaction.
cardano-cli shelley transaction build-raw \
--tx-in 130f907864baccf1b12d9a310bdab94a524bf3c8feb185b353385d7dedd9c7a0#0 \
--tx-out $(cat block-one/addresses/payment1.addr)+9499071025 \
--ttl 585807 \
--fee 171133 \
--tx-body-file block-one/transactions/tx1.txbody \
--certificate-file block-one/addresses/pool-deregistration.certtx1.txbody contains the output raw file.
Step 9: sign the transaction
We use the sender key payment1.skey and cold.skey to sign the transaction file tx1.txbody.
cardano-cli shelley transaction sign \
--tx-body-file block-one/transactions/tx1.txbody \
--signing-key-file block-one/addresses/payment1.skey \
--signing-key-file block-one/keys/cold.skey \
--testnet-magic 42 \
--out-file block-one/transactions/tx1.signedtx1.signed contains the signed transaction file.
Step 10: submit the transaction
We submit the signed transaction file tx1.signed.
cardano-cli shelley transaction submit \
--tx-file block-one/transactions/tx1.signed \
--testnet-magic 42