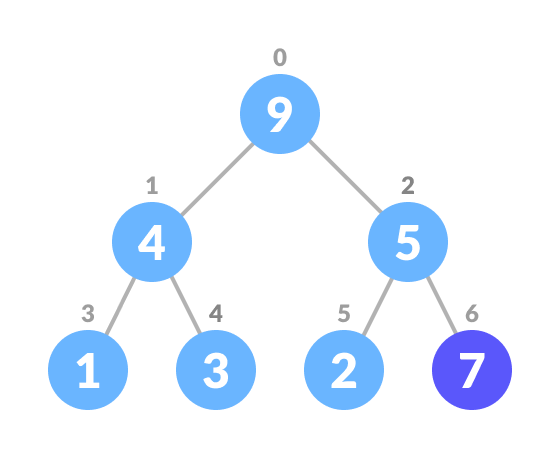
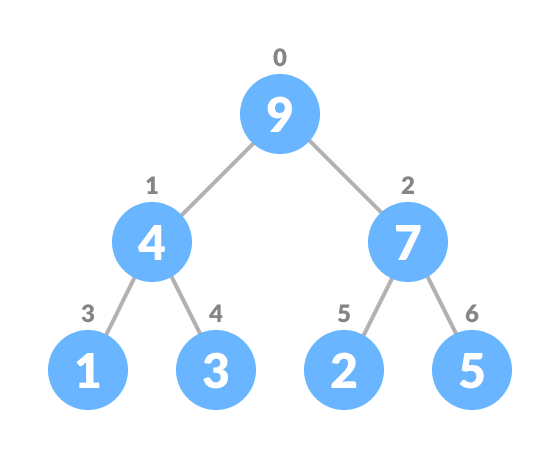
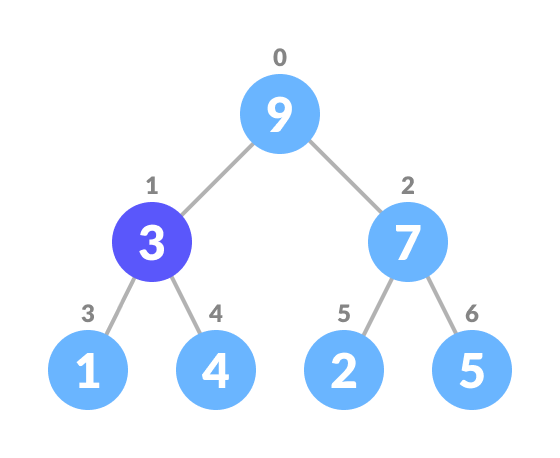
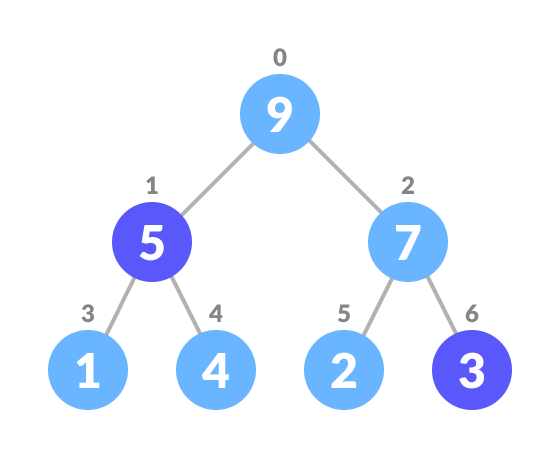
A Heap is a binary tree-based data structure there are two types:
- Max Heap: any node is greater than its children where the parent node always contains the maximum element of this sub-tree
- Min Heap: any node is smaller than its children where the parent node always contains the minimum element of this sub-tree
Heaps maintain data in semi-order. It is a good tradeoff between having to maintain a complete order and searching through random chaos. They allow quick access to the max and min element in O(1) thus they become useful when we want to remove the element with highest/lowest value (priority) quickly ex: in priority queue.
Some of the important operations performed on a heap are described below along with their algorithms.
- Heapify: the process of creating a heap data structure from a binary tree. It is used to create a Min-Heap or a Max-Heap.
Steps:
- Convert the array into a binary tree
- Heapify the tree
To build a binary tree from it the root node will be at index 0 and its children are at the following indices:
- Left child index = 2i + 1
- Right child index = 2i + 2
Note
You might encounter some implementations that use 1-based indexing to simplify calculations, where the root node is at index 1. In that case, the child node formulas would be:
- Left child index: 2i
- Right child index: 2i + 1
- Top down approach
- Bottom up approach
Top down approach: it starts at the root node and heapify all nodes by recursively calling heapify on its children taking time complexity of nlog(n)
The thing is we don't need to heapify all nodes as leaf nodes already satisfy the heap property!
Bottom up approach uses the fact that we only need to heapify the non-leaf nodes it starts at the last non-leaf node and works its way up the tree in reverse level order. resulting in time complexity of O(n) which is more efficient than top down approach.
We can find the index of the last non-leaf node using the following formula : last non-leaf node index = n/2 - 1
Building Heap using bottom up approach:
static void buildHeap(int arr[], int n)
{
// Index of last non-leaf node
int startIndex = (n / 2) - 1;
for (int i = startIndex; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(arr, n, i);
}Heapify function for max heap
void maxHeapify(int arr[], int n, int parent)
{
int largest = parent;
int left = 2 * parent + 1;
int right = 2 * parent + 2;
// If left child is larger than parent
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest])
largest = left;
// If right child is larger than largest so far
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest])
largest = right;
// If largest is no longer the parent
if (largest != parent)
{
std::swap(arr[parent], arr[largest]);
maxHeapify(arr, n, largest);
}
}For minHeapify it is the same process it only differs in the conditions and checks on the root node
void minHeapify(int arr[], int n, int parent) {
int smallest = parent;
int left = 2 * parent + 1;
int right = 2 * parent + 2;
// If left child is smaller than parent
if (left < n && arr[left] < arr[smallest])
smallest = left;
// If right child is smaller than smallest so far
if (right < n && arr[right] < arr[smallest])
smallest = right;
// If smallest is not parent
if (smallest != parent) {
std::swap(arr[parent], arr[smallest]);
minHeapify(arr, n, smallest);
}
}- We insert the new element at the end of the tree and heapify
void insertNode(int arr[], int& n, int key)
{
// Increase the size of Heap by 1
n = n + 1;
// Insert the element at end of Heap
arr[n - 1] = key;
// Heapify the new node following a Bottom-up approach
heapify(arr, n, n - 1);
}Delete process is quite simple:
- Selecting the element we will be deleting
- Swap it with the last element
- Heapify the tree
void deleteNode(int arr[], int& n, int i)
{
// Get the last element
int lastElement = arr[n - 1];
// Replace node at index i with last element
arr[i] = lastElement;
// Decrease size of heap by 1
n = n - 1;
// heapify the modified heap
heapify(arr, n, i);
}| Max Heap | Min Heap | |
|---|---|---|
| Root Value | Largest element | Smallest element |
| Priority | Highest value has highest priority | Lowest value has highest priority |
| First Extracted Value | Maximum value | Minimum value |
| Common Applications | - Priority Queues - Heapsort (ascending order) |
- Dijkstra's Algorithm - Prim's Minimum Spanning Tree - Heapsort (ascending order) |