[摘要] 在这次作业中我们提出了一种新的 Hash Function —— SHA-RNN。其以海绵结构为基础,融合了混沌系统与循环神经网络的特点,可以接受任意长度的串作为输入,并生成长度为 80 比特的消息摘要。我们会对我们的架构进行详细表述,并给出在时间及安全性上的自评估结果。最后,我们会提供完整的实验框架与使用说明。
GitHub Repo 地址:https://github.com/Ashitemaru/Sharnn
**哈希函数(Hash Functions)**是一种将任意长度的消息生成固定长度摘要的映射,其在消息认证、数字签名、身份验证等方面具有十分重要的应用。一般地,我们要求哈希函数具有有效性与安全性,前者是说哈希函数的运作效率要足够快,而后者则对哈希函数的抗原象攻击、抗第二原象攻击等等方面具有一定要求。
**混沌系统(Chaotic System)**的概念最先在物理学中的运动学领域被提出,它是一种非线性系统,其中的值存在着貌似随机的不规则运动,其行为表现为不确定性、不可预测。有部分可以迭代计算的函数可以作为混沌系统的生成函数,比如帐篷函数(Tent Map)。由于混沌系统具有的给定初值输入后,其后生成序列值不可预测,或者说近似服从均匀分布的特点,其可以被用来作为 Hash 函数的重要组成部分。[1]
**循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network)**是一种以序列数据为输入,在序列时序信息的维度上迭代,所有循环单元按链式进行连接的一种递归神经网络。循环神经网络的优势之一,在于其能够在某种程度上“记忆”来自上一个时间状态的信息。如果不同消息分组输入循环神经网络的顺序有先后之别,他们对于同一个“神经元”的作用也有不同的区别。而这种区别,往往是难以用计算追溯到的,也是其相对于简单的全连接层的优势所在。
综合以上三个概念,我们提出了 SHA-RNN,一种新的基于密钥的哈希函数。其采用海绵函数作为基本架构,在每次迭代中使用混沌系统产生近似均匀分布的值作为循环神经网络的权重和偏差。
本篇报告将分为以下几部分。在第 2 节,我们会对我们设计哈希函数时所运用到的关键概念进行简要的回放与讲解。在第 3 节,我们会给出我们所设计的哈希函数的具体参数与详细运作流程。在第 4 节,我们会对我们所设计的哈希函数进行分析,给出在时间效率上和安全性检测上的自评估结果。在附录中,我们会对我们编写的实验框架进行详细的介绍,包括代码介绍与使用方法介绍。
Figure 2.1.1: 海绵函数的示意图Credit: Wikipedia
海绵函数(Sponge Function) [2] 是一种算法,它可以接受任意长度的输入比特流,得到任意长度的输出。它的参数为单次输出比特长度
在吸收阶段,海绵函数单次接受长度为
引用文献 [2] 提出了两种基于密钥的哈希函数,其采用了海绵函数架构,使用了 混沌神经网络(Chaotic Neural Network) 作为海绵函数的状态转移函数
首先我们来对其运作的三个阶段进行简单介绍。(1) 在初始阶段,我们假设输入密钥为
这里的 混沌神经系统 作为海绵函数
我们这里首先引入 Skew Tent Map [4] 的概念,它被广泛地应用于混沌系统的生成当中。Skew Tent Map 是一种迭代函数,它接受上一状态输入
Credit: Citation [3], Figure 3. Figure 2.3.1 Skew Tent Mapping
Credit: Research Gate
我们所提出的哈希函数架构采用海绵函数作为基础,采用的基本架构与图片 2.2.1 类似。不过,我们会详细介绍我们针对其中的参数配置。
在这里我们定义我们海绵函数以及其他部件所使用的常数。
-
RNN 层属性
- 单次输入长度
$r$ :$136$ 字节 - 隐藏状态大小
$r+c$ :$136+64$ 字节 - 单次输出大小:$32$ 字节
- 单次输入长度
-
哈希函数属性
- 哈希函数输出长度:$80$ 比特(对单次输出做高位截断)
-
用户可以设置的参数,以及我们的预置配置,用户可以通过修改源码重新编译得到新的配置
-
混沌系统偏移量
$Q$ :0x789ABCDE -
输入密钥:$K_m$
-
混沌系统生成种子
$K_s$ :0x10 -
混沌系统构建迭代次数
$U_s$ :$10$ -
非线性层迭代次数
$N_r$ :$8$
-
在初始化阶段,我们对原始消息进行填充。对于一条原始消息
然后,我们将填充后的消息
可以将一个混沌系统看成一个混沌状态发生器,或者将其视为是一个满足如下条件的映射: $$ \operatorname{DSTMap}{Q} X(n+1)= \begin{cases}2^{N} \cdot \dfrac{X(n)}{Q} & 0<X(n-1)<Q \ 2^{N}-1 & X(n-1)=Q \ 2^{N} \cdot \dfrac{2^{N}-X(n)}{2^{N}-Q} & Q<X(n-1)<2^{N}\end{cases} $$ 对于给定的 32 比特数 $N$ 与上一状态 $X(n)$,我们通过上述函数将其转化为 $X(n+1)$,该映射满足点列 ${X(i)}{i=0}^{\infin}$ 近似均匀随机。
此外,我们还可以定义类似的运算: $$ \operatorname{DPWLCMap}_Q (X(n))= \begin{cases}2^{N} \cdot \dfrac{X(n-1)}{Q} & 0<X(n-1) \leq Q \ 2^{N} \cdot \dfrac{X(n-1)-Q}{2^{N-1}-Q} & Q<X(n-1) \leq 2^{N-1} \ 2^{N} \cdot \dfrac{2^{N}-X(n-1)-Q}{2^{N-1}-Q} & 2^{N-1}<X(n-1) \leq 2^{N}-Q \ 2^{N} \cdot \dfrac{2^{N}-X(n-1)}{Q} & 2^{N}-Q<X(n-1) \leq 2^{N}-1 \ 2^{N}-1-Q & \text { otherwise; }\end{cases} $$ 这个函数将被用于我们非线性的激活函数。
系统初始化时,需要给定参数
我们的 Chaotic Neural Network 采用 RNN 架构。下面对其进行介绍。每个 RNN 架构配有一个混沌状态发生器
由于我们指定了 RNN 架构的输入为
我们定义两种神经元,一种是 RNN Cell,另一种是 Non-linear Cell。RNN Cell 共有 10 个,每个可以接受 160 比特的消息输入和 32 比特的上一状态输入,输出为 32 个比特的当前状态。Non-linear Cell 的输入为 320 比特,输出为 1600 比特。
接下来我们描述一次 RNN 架构的运作流程。
首先设
然后我们将 RNN Cell Layer 输出的 320 比特经过非线性激活层,便得到这次 RNN 层海绵函数状态转移的终态的 1600 比特。
每一个 RNN 神经元接受 160 个比特的串作为输入,这里将其记为
非线性层负责将 320 比特的输出升采样成 1600 比特。其包含的 Cell,我们将其记为
我们首先定义一些基本运算,这里借鉴了参考资料 [2]:
$$
\left{\begin{array}{l}
\operatorname{Maj}\left(D_{1}, D_{2}, D_{3}\right)=\left(D_{1} \wedge D_{2}\right) \oplus\left(D_{1} \wedge D_{3}\right) \oplus\left(D_{2} \wedge D_{3}\right) \
{\rm Ch}\left(D_{1}, D_{2}, D_{3}\right)=\left(D_{1} \wedge D_{2}\right) \oplus\left(\neg D_{1} \wedge D_{3}\right) \
\Sigma 0\left(D_{1}\right)=\operatorname{ROTR}^{2}\left(D_{1}\right) \oplus \operatorname{ROTR}^{13}\left(D_{1}\right) \oplus \operatorname{ROTR}^{22}\left(D_{1}\right) \
\Sigma 1\left(D_{3}\right)=\operatorname{ROTR}^{6}\left(D_{3}\right) \oplus \operatorname{ROTR}^{11}\left(D_{3}\right) \oplus \operatorname{ROTR}^{25}\left(D_{3}\right) \
\operatorname{ROTR}^{n}(x)=(x \gg n) \vee(x \ll(32-n))
\end{array}\right.
$$
${\rm Cell}{5-8}$ 负责完成维度上的升采样过程,其接受 160 比特的串作为输入,输出为 256 比特,其计算方式为:
$$
\left{\begin{array}{l}
H{0}=D_{0} \oplus t_{1} \oplus {\rm Maj}\left(D_{1}, D_{2}, D_{3}\right) \oplus \Sigma 0\left(D_{1}\right) \
H_{1}=t_{1} \oplus D_{0} \
H_{2}=D_{0} \oplus D_{1}, H_{3}=D_{1} \oplus D_{2}, H_{4}=D_{2} \oplus D_{3} \
H_{5}=D_{0} \oplus D_{1} \oplus t_{1} \
H_{6}=D_{1} \oplus D_{2} \oplus t_{1} \
H_{7}=D_{2} \oplus D_{3} \oplus t_{1} \
\text { where } t_{1}={\rm Ch}\left(D_{1}, D_{2}, D_{3}\right) \oplus D_{4} \oplus \Sigma 1\left(D_{3}\right)
\end{array}\right.
$$
非线性激活层首先定义
然后,对这个结果的前 5 个 32 比特迭代重复
对输入的每个 160 比特经过 ${\rm Cell}{5-8}$ 升采样为 256 比特,然后将结果经过 $N_r$ 次迭代后,作为结果输出后级联得到 512 个比特。然后再将该结果经过 ${\rm Cell}{8-8}$ 每迭代一次,生成 512 比特后级联,直到结果超过 1600 比特后取前 1600 比特。之后,每次从结果中提取 64 比特,然后再进行迭代,直到满足输出条件长度后截断。
我们对于大小分别为
我们的实验环境为:
- 处理器 Intel64 Family 6 Model 141 Stepping 1 GenuineIntel ~2688 Mhz(Intel-i5)
- 内存:16 GB
- 操作系统:Windows WSL2(Ubuntu 20.04)
我们使用NIST提供的 Statistical Test Suite 对哈希结果的随机性进行检测。
首先生成哈希序列。在
| 编号 | 测试类型 | 通过率 | p 值均匀性$^3$ | 非默认参数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Frequency | 111/111 | 0.580520 | - |
| 02 | Block Frequency | 20758/20971 | 0.273558 | |
| 03 | Cumulative Sums | 2/2$^1$ | 通过$^1$ | - |
| 04 | Runs | 111/111 | 0.263452 | - |
| 05 | Longest Run of Ones | 109/111 | 0.656043 | - |
| 06 | Rank | 109/111 | 0.328861 | - |
| 07 | Discrete Fourier Transform | 111/111 | 0.674920 | - |
| 08 | Nonperiodic Template Matchings | N/A$^4$ | N/A$^4$ | N/A$^4$ |
| 09 | Overlapping Template Matchings | 111/111 | 0.003401 | |
| 10 | Universal Statistical | 54/55 | 0.719747 |
|
| 11 | Approximate Entropy | 110/111 | 0.000086$^2$ | |
| 12 | Random Excursions | 8/8$^1$ | 通过$^1$ | - |
| 13 | Random Excursions Variant | 18/18$^1$ | 通过$^1$ | - |
| 14 | Serial | 2/2$^1$ | 通过$^1$ | |
| 15 | Linear Complexity | 110/111 | 0.818179 | - |
注:
- 表示该检测度量有多个指标
- 表示该指标的
$p$ 值过小,表示$p$ 值分布不提示均匀分布 - p 值大于
$10^{-4}$ 表示通过 - 由于本次作业要求哈希结果的位数过少,本测试我们未能找到合适的测试参数
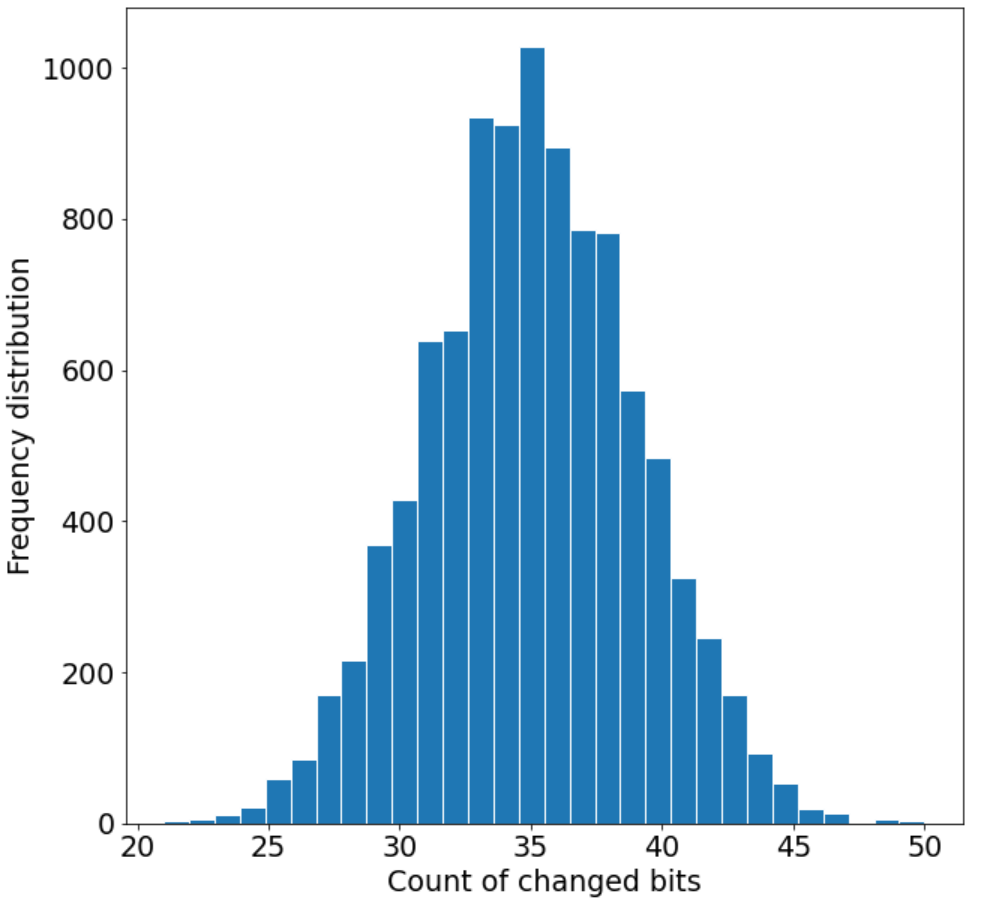
为了度量哈希的扩散效果,我们对 SHA-RNN 算法进行了扩散测试
-
输入串
$M$ ,计算哈希值$H_1$ ,对于$M$ 我们选取 Wikipedia 中对海绵结构的介绍In cryptography, a sponge function or sponge construction is any of a class of algorithms with finite internal state that take an input bit stream of any length and produce an output bit stream of any desired length. Sponge functions have both theoretical and practical uses. They can be used to model or implement many cryptographic primitives, including cryptographic hashes, message authentication codes, mask generation functions, stream ciphers, pseudo-random number generators, and authenticated encryption. Sponge functions have both theoretical and practical uses. In theoretical cryptanalysis, a random sponge function is a sponge construction where f is a random permutation or transformation, as appropriate. Random sponge functions capture more of the practical limitations of cryptographic primitives than does the widely used random oracle model, in particular the finite internal state.
-
对串
$M$ 随机选取一位进行翻转,然后再计算哈希值$H'$ -
计算
$H$ 和$H'$ 中不同有位数的数量$B_i$
将上述过程在 SHA-RNN 算法中重复
定量计算
-
改变位数的最小值
$B_{\min }=\min \left(\left{B_{i}\right}_{i=1, \ldots, N}\right)$ -
改变位数的最大值
$B_{\max }=\max \left(\left{B_{i}\right}_{i=1, \ldots, N}\right)$ -
改变位数的标准差
$\Delta B=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{N-1} \sum_{i=1}^{N}\left(B_{i}-\bar{B}\right)^{2}}$ -
改变位数的平均值
$\bar{B}=\dfrac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} B_{i}$ -
每位的改变概率
$P=\left(\dfrac{\bar{B}}{80}\right) \times 100 %$
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 标准差 | 平均值 | 每位变化概率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 50 | 4.14 | 35.00 | 43.75% |
我们混沌系统采用的发生函数 $\text{DSTMap}Q$ 可以很好地起到生成均匀分布的数据的目的。我们这里对 STMap 做了实验,取 $\mu = 1, Q=0.3$,然后对输出函数 $\text{STMap}{0.3}$ 做傅里叶变换后得到上图,可以看出数据具有较强的随机性,满足均匀分布的条件。
[1] LIU J, FU X. Spatiotemporal chaotic one-way hash function construction based on coupled tent maps[J]. Journal on communications, 2007, 28(6): 34.
[2] Bertoni G, Daemen J, Peeters M, et al. Sponge functions[C]//ECRYPT hash workshop. 2007, 2007(9).
[3] Abdoun N, El Assad S, Manh Hoang T, et al. Designing two secure keyed hash functions based on sponge construction and the chaotic neural network[J]. Entropy, 2020, 22(9): 1012.
[4] Hasler M, Maistrenko Y L. An introduction to the synchronization of chaotic systems: coupled skew tent maps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 1997, 44(10): 856-866.
[5] Penard W, van Werkhoven T. On the secure hash algorithm family[J]. Cryptography in context, 2008: 1-18.
[6] Smid E B, Leigh S, Levenson M, et al. A statistical test suite for random and pseudorandom number generators for cryptographic applications[J]. Her research interest includes Computer security, secure operating systems, Access control, Distributed systems, Intrusion detection systems, 2010.
实验框架使用方法介绍如下:
# Build
./run.sh
# Usage
bin/SHA-RNN # (1) Input Mode
bin/SHA-RNN -f <file_path> # (2) Hash file
bin/SHA-RNN -s <string> # (3) Hash string实验框架介绍如下:
.
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── bin
│ ├── SHA-RNN # 主程序
│ ├── test1 # Basic Usage Test
│ ├── test2 # Consistency Test
│ ├── test3 # Perf Test
│ └── test4 # Diffusion Test
├── include
│ └── define.h
├── main.cpp
├── readme.md
├── readme.pdf
├── run.sh
├── src
│ ├── Bitset.hpp # 比特流
│ ├── ChaoticMap.hpp # DSTMap / DPWLCMap
│ ├── ChaoticSystem.hpp # 混沌系统
│ ├── NonLinear.hpp # 非线性激活层
│ ├── PaddedStream.hpp # 对输入串填充
│ ├── RNN.hpp # RNN 架构
│ ├── RNNHash.hpp # 派生自 SpongeHash,负责调用 RNN 架构的逻辑
│ └── SpongeHash.hpp # 海绵结构
├── statistics
│ ├── Makefile
│ ├── analyze.ipynb # 扩散数据分析
│ ├── diffusion.cpp # 扩散数据生成
│ ├── eval.py # NIST 随机性测试脚本
│ ├── sample.cpp # 随机性测试采样
│ └── text.in # 扩散测试样本数据
└── test
├── test1.cpp # Basic Usage Test
├── test2.cpp # Consistency Test
├── test3.cpp # Perf Test
└── test4.cpp # Diffusion Test